Uganda
Politics
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, obtained formal independence from UK on October 9, 1962. In October 1963, Uganda became a republic but maintained its membership in the Commonwealth of Nations. Uganda is a presidential republic, in which the President of Uganda is both the head of state and head of government. (5) The current president is Yoweri Museveni, who has served as President of Uganda since 1986 and allegedly won re-election for a sixth term on 16 January 2021 by the electoral commission of Uganda with 58.6% of the vote.
Official languages
The official languages of Uganda are English and Swahili. In the most developed central area (Kingdom of Buganda) the common language is Luganda.
Population
Based on Ugandan statistics, the total population of Uganda is 46.4 million by 2024(2), of which over 26% is urban population (3).
Figure IV: Uganda Population (4)
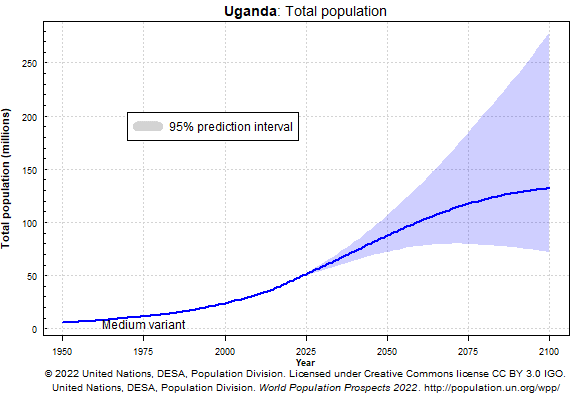
Figure V: Percentage of Population in Urban and Rural Areas in Uganda (5)

Ethnic group
Uganda is populated by dozens of ethnic groups. The Baganda make up the largest ethnic group in Uganda, though they represent only around 17% of the population (6).
Figure VI: Population Distribution by Ethnicity in Uganda

Religions
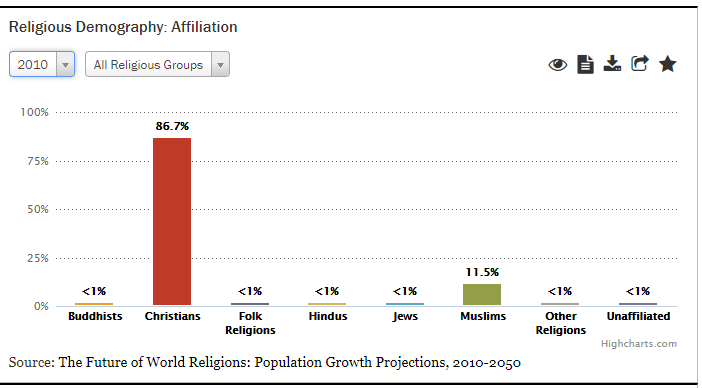
Uganda is a religiously diverse nation with Christianity being the most widely professed faith. According to recent census, conducted in 2014, 84% of the population is Christian (7). The largest Christian group is Catholic at 39% of the population, 32% are Anglican, and 11% are Pentecostal Christian (8).
Figure VII: Population Distribution by Religion in Uganda

Health
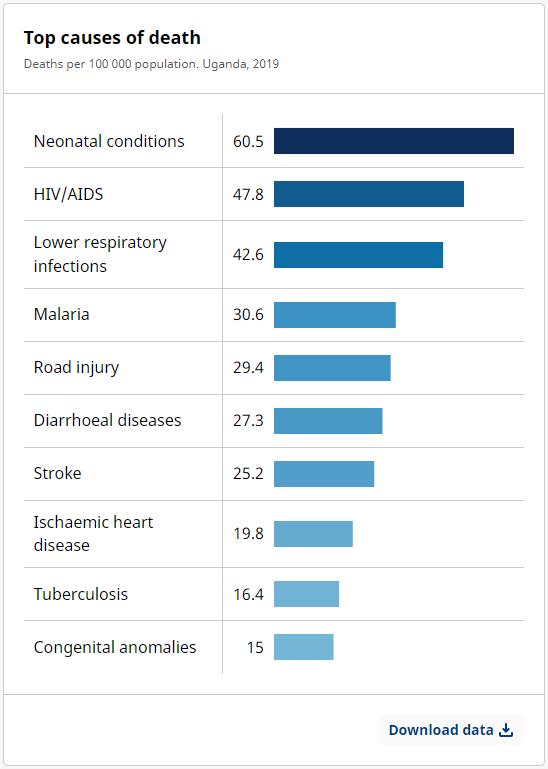
In Uganda, life expectancy at birth (years) has improved by 17.2 years from 48.8 years in 2000 to 66 years in 2021. The top three leading causes of death in Uganda recorded in 2019 are neonatal conditions, AIDS and lower respiratory infections. Malaria and tuberculosis impact also heavily the country’s health situation (9).
Economy
With the ravages of a countrywide AIDS epidemic and threatening Malaria, the economy growth is hindered for many years, Uganda's economy grew at a slow pace. In 2024, the GDP of Uganda reached 57.9 billion USD with a growth rate of 5.7%. The figure of GDP per Capita was 1250USD (10).
In 2022, among all of the business sectors, agriculture contributed 24.01% to the Uganda's GDP, 26.77% came from the industry. The vast majority of the Uganda's GDP was generated by the Services and other activity sectors, which was 41.65% (11).
Figure VII the distribution of the GDP across economic sectors in Uganda from 2009 to 2022 (10)

From the above table we can see that during the last decade the economy of Uganda transformed slowly towards service economy from agricultural economy. VFLBO supports the development towards more industry. However, the very fertile Ugandan soil and the availability of plenty of water suggest a stronger development of the agricultural sector with the aim to process more coffee and other agricultural products.
Education
In 1997 the Ugandan government introduced universal primary education (the idea that all children should be able to attend primary school for free) and in 2007 universal secondary education. By 2022, the literacy rate of people ages 15 and above reached 81% (12).
In reality, VFLBO was shocked by the standards of Ugandan Schools. Most Ugandans wish to send their kids to costly private schools. VFLBO wishes to help ensure real education. Many schools are more business enterprises than educational institutions.
Sources
1 Figures from Wikipedia
2 https://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/profile/UGA
3 https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.URB.TOTL?locations=UG
4 https://population.un.org/wpp/Graphs/DemographicProfiles/Line/800
5 https://population.un.org/wup/Country-Profiles/
6 https://www.nationmaster.com/country-info/stats/People/Ethnic-groups
7 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Religion_in_Uganda
8 https://www.state.gov/reports/2022-report-on-international-religious-freedom/uganda/
9 https://data.who.int/countries/800
10 https://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/profile/UGA12
11 https://www.statista.com/statistics/447716/uganda-gdp-distribution-across-economic-sectors/
12 https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SE.ADT.LITR.ZS?locations=UG





















